New Window into the birth of massive stars: The IVARS Project Demonstrates High-Cadence Radio Monitoring of Massive Protostars

An international team of astronomers has successfully completed the IVARS (Interferometer for Variable Astrophysical Radio Sources) project, delivering a new observational capability for studying the formation of massive stars through time-variable radio emission. By combining two radio telescopes at the Irbene Radio Observatory in Latvia into a dedicated single-baseline interferometer, the project has enabled the first sustained, high-cadence monitoring of radio continuum variability in high-mass protostars, carried out simultaneously with maser monitoring.
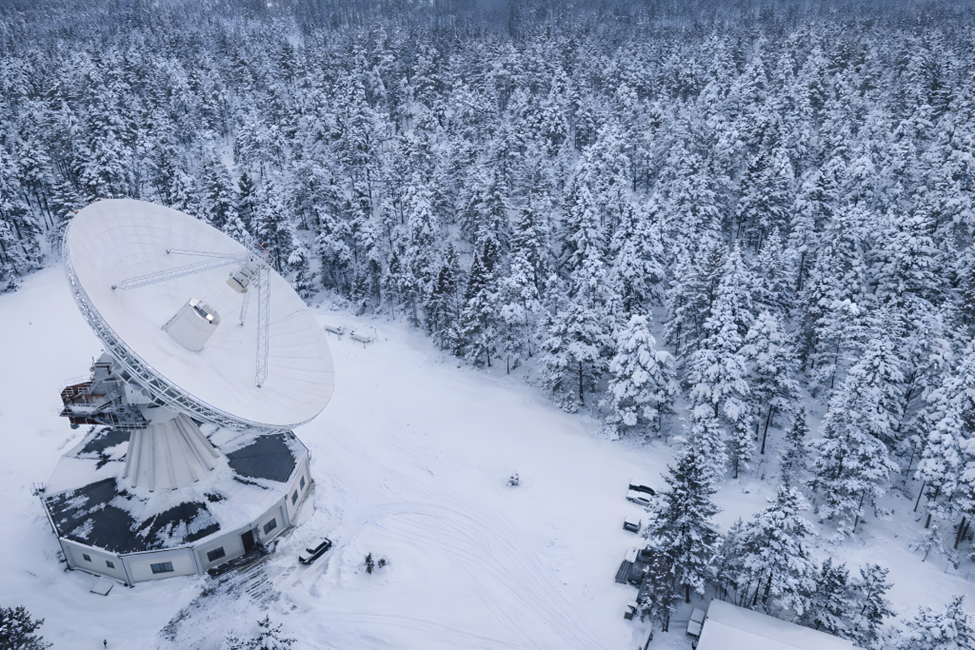

Irbene RT-32 antenna (Photo by Roberts Rasmanis)
High-mass stars shape the evolution of galaxies through their radiation, winds, and eventual supernovae, yet their formation remains poorly understood. Growing evidence suggests that these stars do not grow steadily, but instead undergo episodic accretion bursts. Such events leave signatures in both molecular maser emission and weak radio continuum emission, evolving on timescales from days to years. Capturing these changes requires frequent, sensitive observations over long periods which is a mode of observing that is difficult to achieve with large, oversubscribed radio telescope arrays. The IVARS project was designed to address this gap.
A dedicated interferometer for time-domain astrophysics
IVARS transformed the 32-m and 16-m Irbene radio telescopes, operated by the Ventspils International Radio Astronomy Centre (VIRAC), into an 800-m single-baseline interferometer optimized for time-domain radio astronomy. Unlike large interferometric arrays that prioritize snapshot imaging, this configuration allows repeated observations of the same sources at fixed geometries, delivering stable and repeatable measurements of weak, extended emission.
A key technical achievement of the project was the restoration and stabilization of interferometric operations through the deployment of a hydrogen maser clock and a White Rabbit time-transfer system, enabling nanosecond-level synchronization between the two antennas. This was paired with a fully automated observing, correlation, and calibration workflow, allowing the system to operate reliably over long monitoring campaigns.
Scientific highlights
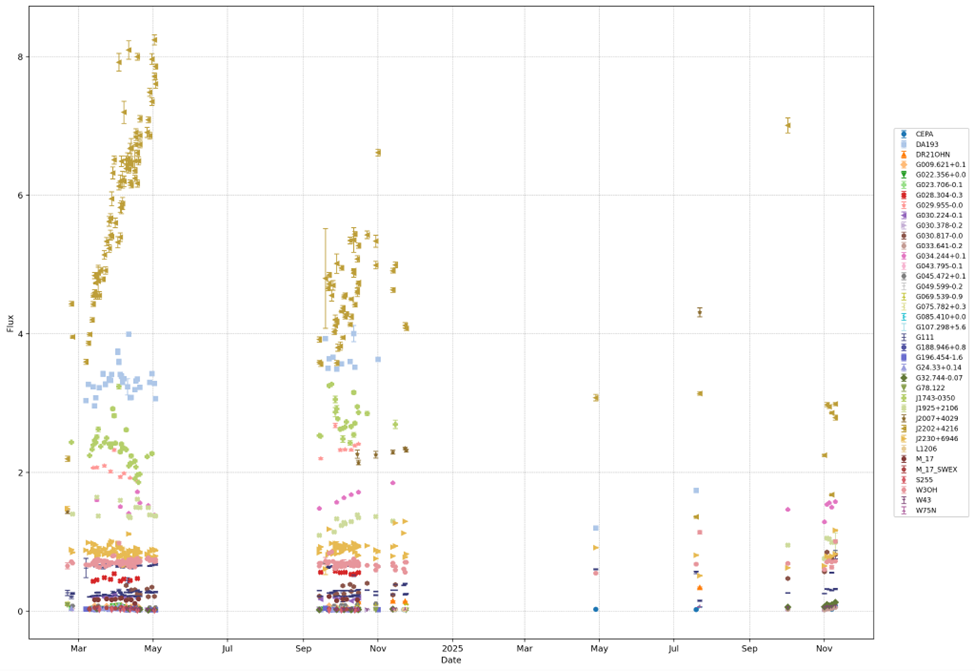
Over the course of the project, IVARS monitored a sample of 30 high-mass protostars known to host 6.7 GHz methanol masers. Of the 30 targets, continuum emission was detected in 16 sources, with 14 non-detections. Maser emission was detected in 26 targets. Maser and continuum emission were also detected in two high-mass protostars which were used as brightness calibrators.
Overall the campaign achieved several notable results:
- Detection of radio continuum variability in multiple high-mass protostars, demonstrating that weak continuum emission (10s of millijansky) from forming massive stars can be monitored reliably at high cadence using a single-baseline interferometer.
- Simultaneous maser and continuum monitoring, providing a unique dataset that links maser flares and continuum variability within the same sources.
- Identification of maser flaring events, including rapid changes seen over several spectral line components consistent with episodic accretion phenomena.
- High-resolution follow-up observations with the European VLBI Network (EVN) for selected targets, revealing disk- and outflow-related maser morphologies at milliarcsecond scales.
- High-cadence monitoring of BL-Lac, revealing a large radio flare in the well known prototypical blazar source at very high time resolution.
Validation of automation-driven interferometry, showing that complex interferometric observing and processing can be executed with minimal manual intervention.
At present, the single-baseline radio interferometer developed by the IVARS project, represents the only infrastructure worldwide that enables high-cadence radio continuum monitoring of high-mass protostellar objects together with simultaneous maser observations.
Software and infrastructure with lasting impact
Beyond its scientific output, IVARS delivered a suite of openly available software tools. Central among these is the Automatic Correlation (ACor) system, a web-based platform that automates observation scheduling, data transfer, correlation, calibration, and quality assessment. Designed to be observatory-agnostic, ACor and the associated data-processing pipelines can be adapted by other facilities operating small interferometers.
These tools have already been adopted within VIRAC for additional science programs, including stellar flare and active galactic nucleus monitoring, and are being shared with international collaborators.
Empowering the next generation
IVARS also played a significant role in education and capacity building. Project members supervised bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral theses, contributed to the enhancement of radio astronomy related academic and research activity at the University of Latvia, and trained students in interferometric data processing through hands-on work and international research visits. Several early-career researchers involved in the project have since progressed to doctoral or postdoctoral positions, carrying forward the expertise developed within IVARS.
Public engagement formed another pillar of the project, with team members delivering lectures, media interviews, and outreach activities aimed at secondary-school students and the general public, helping to raise awareness of radio astronomy and time-domain astrophysics.
Looking ahead
While the IVARS project has formally concluded, the pursuit of its scientific program continues. An international working group focused on single-baseline radio interferometric projects, based on IVARS, is being planned. The team is exploring how the single-baseline interferometer approach pioneered by IVARS can be replicated at other observatories worldwide, forming the basis for a broader international community focused on time-domain radio interferometry.
By demonstrating that modest-sized radio telescopes, when carefully configured and automated, can deliver unique scientific insights, IVARS has opened a new observational window on the dynamic processes governing the birth of the most massive stars in our Galaxy.
The scientific results are presented in the following publications:
- An Interferometer for Variable Astrophysical Radio Sources, Journal of Astronomical Telescopes, Instruments, and Systems (JATIS);
- Applications of the Irbene Single-Baseline Radio Interferometer, Galaxies 2025;
- A millimeter methanol maser ring tracing the deceleration of the heat wave powered by the massive protostellar accretion outburst in G358.93-0.03 MM1, Astrophysical Journal Letters;
- Search for the optimal smoothing method to improve S/N in cosmic maser spectra, Open Astronomy 2025;
- 6.7 GHz methanol masers in three HMYSOs: G37.43+01.51, G37.479$-$0.105 and G37.55$+$0.20, A&A (accepted for publishing)
- IVARS Project source monitoring summary manuscript (in preparation)
All developed software is open-source and available for use:
1) Automatic Correlation (ACor) information system (GitHub repository and ASCL.net);
This project received funding from the Latvian Council of Science project “A single-baseline radio interferometer in a new age of transient astrophysics (IVARS)”, No. lzp-2022/1-0083.
Share on other platforms
Other news







